Music is a magical language that everyone around the world can understand. There are over 1,500 different musical instruments out there, each with its own special sound and story. Imagine early humans using bones and sticks to make music. Fast forward to today, and we’ve got high-tech gadgets like electronic synthesizers that can make all sorts of cool sounds.
The musical instruments covered in our blog post might not be as famous as guitars or pianos, but they have their own amazing stories and unique sounds. It’s like discovering a secret level in your favorite video game!
This post contains affiliate links. Please read our disclosure.
Musical Instruments FAQ
1. What defines a musical instrument as ‘rare’?
2. What is the oldest known musical instrument?
3. How have musical instruments evolved over time?
Musical Instrument Families
Physical instruments are broadly categorized into several families based on their method of sound production. The string family, including instruments like the violin, guitar, and harp, produces sound through the vibration of strings. Woodwind instruments, such as the flute, clarinet, and saxophone, generate sound by blowing air through a reed or across an opening. The brass family, encompassing the trumpet, trombone, and tuba, creates music through the vibration of the player’s lips on a mouthpiece. Percussion instruments, like drums, xylophones, and tambourines, produce sound when struck, shaken, or scraped. Keyboard instruments such as the piano and organ use a combination of strings and hammers or air to generate sound. In the modern era, electronic instruments like synthesizers and electric guitars have emerged, utilizing electronic circuits to produce a wide range of sounds. Each family of instruments enriches the mosaic of musical expression.
| Instrument Family | Examples |
|---|---|
| String | Violin, Guitar, Harp |
| Woodwind | Flute, Clarinet, Saxophone |
| Brass | Trumpet, Trombone, Tuba |
| Percussion | Drums, Xylophone, Tambourine |
| Keyboard | Piano, Organ |
| Electronic | Synthesizers, Electric Guitar |
Learning about rare musical instruments helps us appreciate the diversity and richness of musical traditions around the world. It also provides insights into the cultural heritage and innovations of different societies.
Learning about rare musical instruments helps us appreciate the diversity and richness of musical traditions around the world. It also provides insights into the cultural heritage and innovations of different societies.
The following are among some of the rarest musical instruments you’ve probably never heard of, and which are sure to surprise and delight you.
1. Ondes Martenot
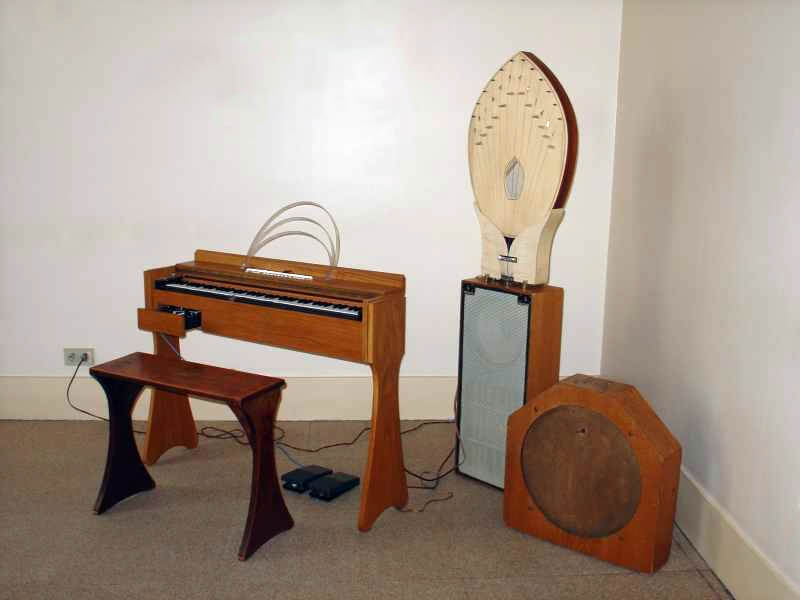

The Ondes Martenot is an early electronic musical instrument invented in 1928. It features a keyboard and a sliding wire to create vibrato effects, producing eerie and ethereal sounds similar to a theremin. The instrument has been used in classical compositions, film scores, and experimental music due to its expressive capabilities.
2. Kalimba
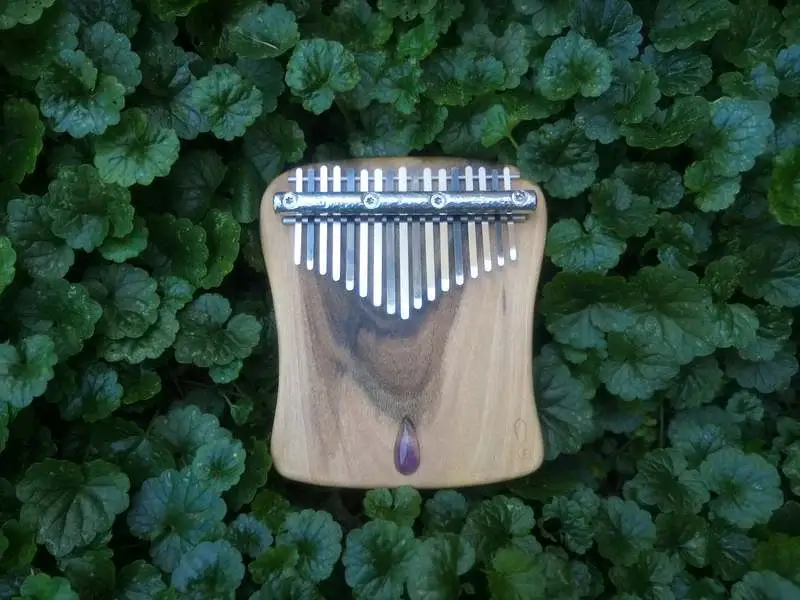

The Kalimba, also known as a thumb piano, is a traditional African musical instrument. It consists of a wooden board (often hollow) with metal tines of varying lengths attached to the top. The tines are plucked with the thumbs to produce music. Each tine has a different pitch, determined by its length and thickness, allowing the player to create melodies and harmonies. The Kalimba has its roots in African culture and has been used for centuries in various forms across the continent. It is known for its soothing, bell-like tones and is often used in spiritual and ceremonial contexts.
3. Octobass
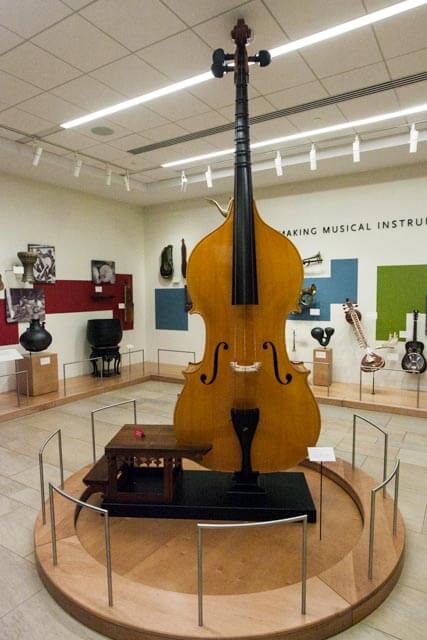

The Octobass is an exceptionally large string instrument designed in the 19th century. It stands over three meters tall and produces extremely low frequencies, extending the range of the double bass into subsonic realms. Due to its massive size and specialized playing technique, it is rarely seen outside of orchestral performances of certain classical compositions.
4. Seraphine
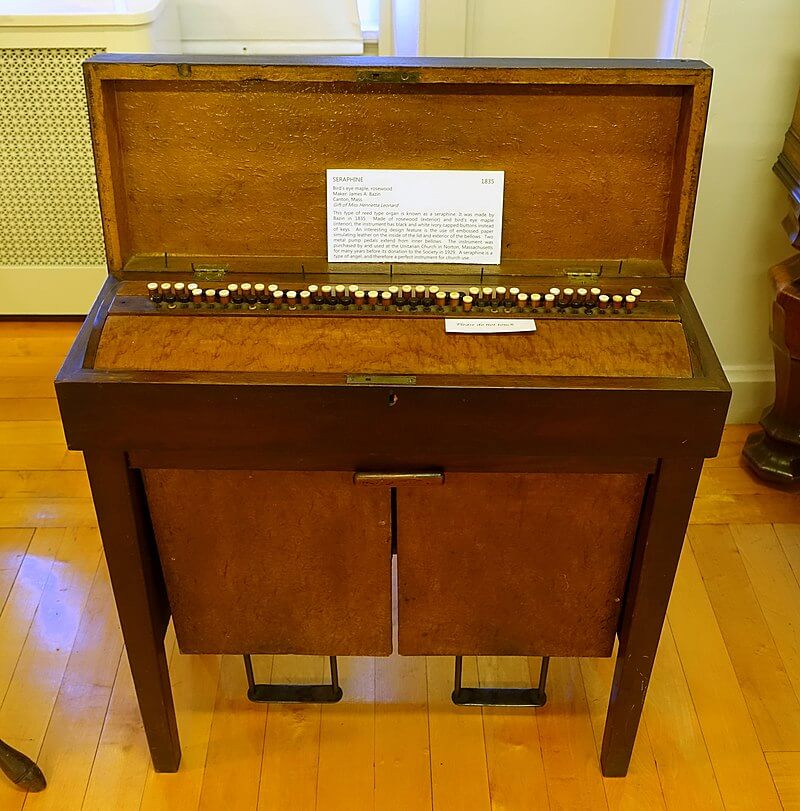

The Seraphine is a rare keyboard instrument resembling a small piano but with strings that are struck rather than plucked. It was invented in the 18th century and was popular for its unique sound, somewhere between a harpsichord and a dulcimer. The seraphine fell out of favor in the 19th century but has seen occasional revivals among enthusiasts of historical keyboard instruments.
5. Trombone

The Trombone has a cylindrical bore and usually features a bell that flares outwards. It’s a versatile instrument capable of playing both melody and harmony parts in ensembles, and it’s valued for its expressive capabilities and wide range. The Trombone is a staple in various musical genres, including classical orchestras, concert bands, jazz ensembles, and contemporary music. In orchestral settings, it often plays a crucial role in brass sections, providing both harmonic support and lyrical solos.
6. Kraakdoos
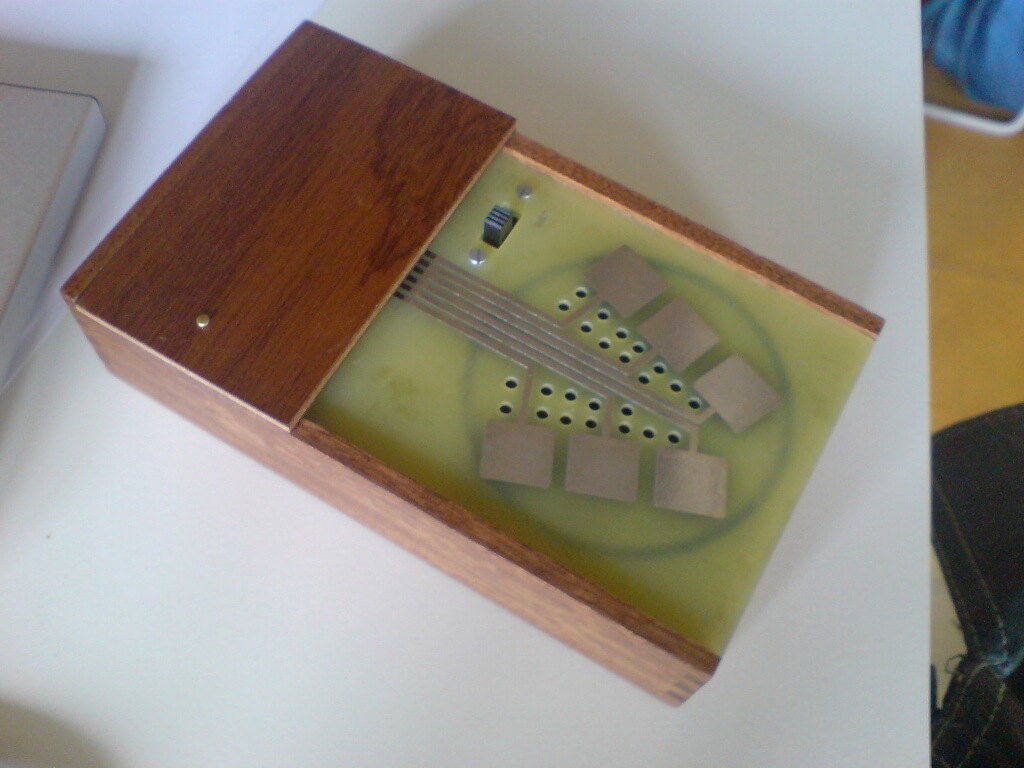

The Kraakdoos is a pocket-sized electronic noise maker, developed in the 1970s. It features various electronic circuits that generate unpredictable and noisy sounds, often used in experimental music and sound art. The Kraakdoos is prized for its ability to create unique textures and timbres, making it a favorite among avant-garde musicians and electronic composers.
7. Stalacpipe Organ
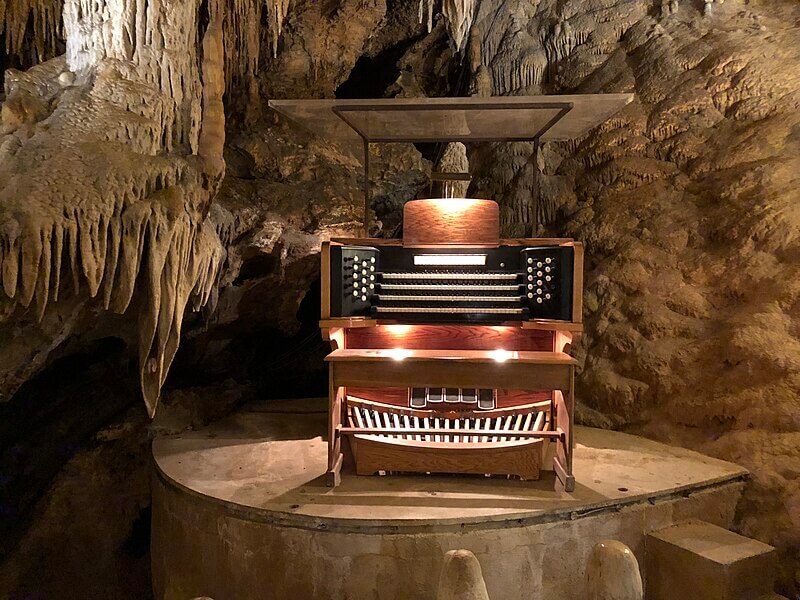

The Stalacpipe Organ is a unique musical instrument located in Virginia’s Luray Caverns. It uses naturally formed stalactites, struck by rubber mallets, to produce tones. Each stalactite is carefully tuned to create a scale, allowing the organist to play melodies and chords deep within the cavern’s natural acoustics. This remarkable instrument combines music with the awe-inspiring beauty of underground formations, offering a one-of-a-kind musical experience. The Stalacpipe Organ exemplifies the creative ways humans have harnessed natural elements to create art and music, making it a must-see for visitors exploring the intersection of nature and culture.
8. Hammered Dulcimer
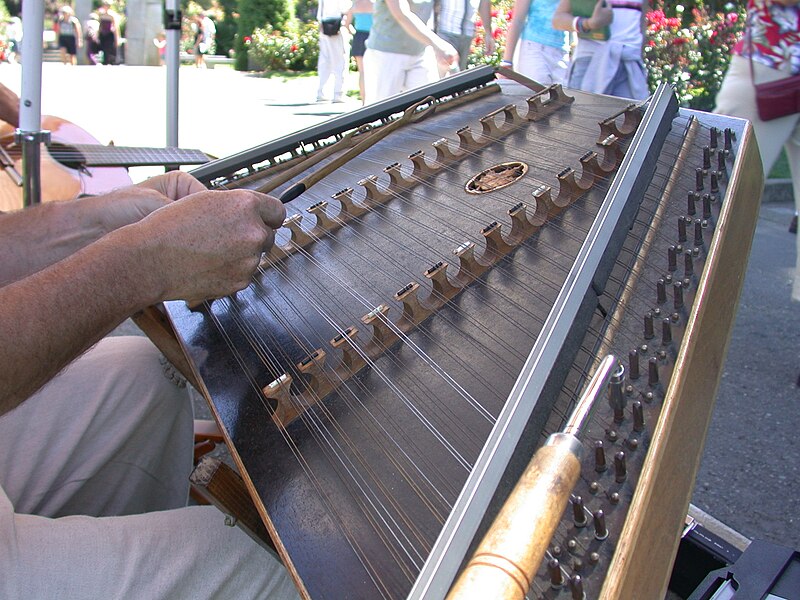

The Hammered Dulcimer is a trapezoidal-shaped string instrument played by striking the strings with small hammers. It is found in various forms across the world, from the Middle East to Eastern Europe and the Americas. The Hammered Dulcimer is known for its bright, bell-like tones, and is popular in folk and classical music, as well as contemporary genres like new-age and world music.
9. Glass Armonica
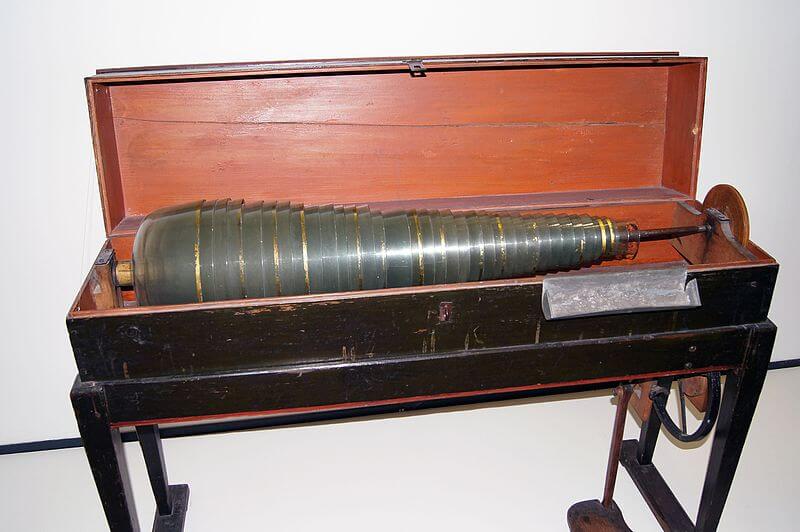

The Glass Armonica is an unusual instrument invented by Benjamin Franklin in the 18th century. It consists of a series of glass bowls or goblets of graduated sizes mounted on a spindle and played by rubbing moistened fingers along the rims. The instrument produces hauntingly beautiful tones with a characteristic ethereal quality. The Glass Armonica was popular in the late 18th and early 19th centuries but fell out of favor due to concerns over the potential health effects of leaded glass bowls. It has since seen occasional revivals and is appreciated for its unique sound in classical and experimental music.
10. Cristal Baschet
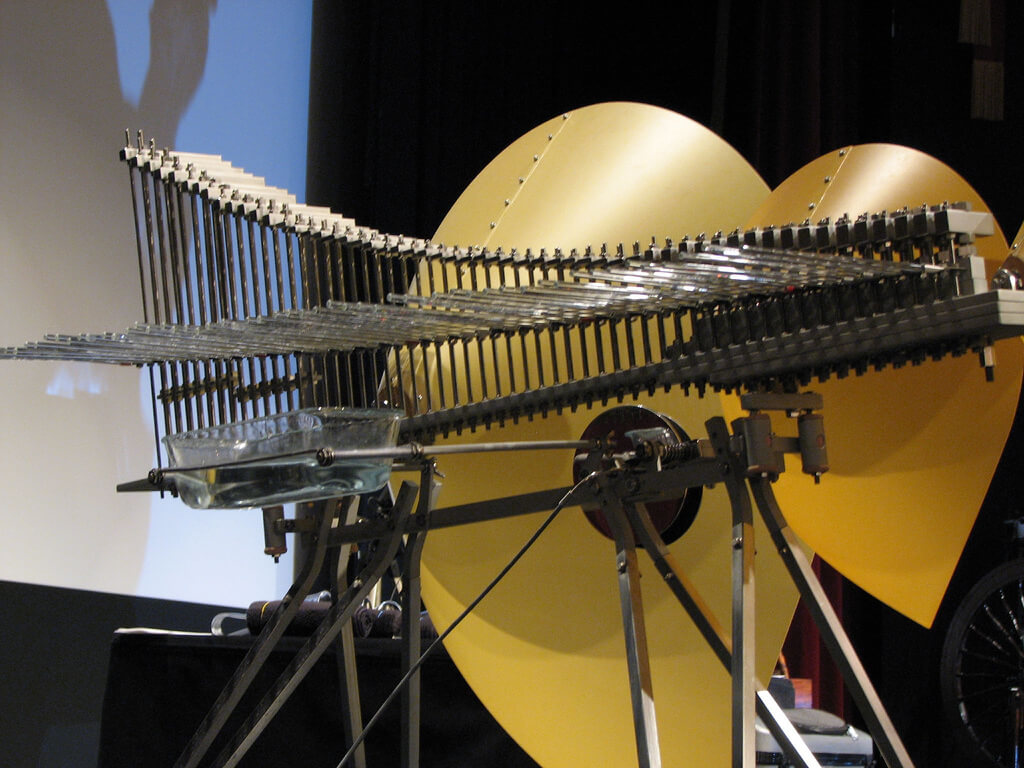
The Cristal Baschet is a contemporary musical instrument invented in the 1950s by French brothers Bernard and François Baschet. It consists of metal rods of different lengths attached to a resonating chamber with a system of amplification using a vibrating plate. The player rubs the rods with wet fingers to create sounds similar to those of a glass harmonica or singing bowl. The Cristal Baschet produces a wide range of ethereal, metallic tones and is used in experimental music, film scores, and contemporary classical compositions for its unique timbre and expressive capabilities.
11. Contrabassoon
The Contrabassoon is a double reed woodwind instrument and the largest and lowest-pitched member of the bassoon family. It plays an octave lower than the bassoon and produces deep, resonant tones. The Contrabassoon is characterized by its long, curved shape and double reed mouthpiece, which vibrates when air is blown through it. It is used primarily in orchestral and wind ensemble music, adding a rich bass foundation to the woodwind section.
12. Shamisen
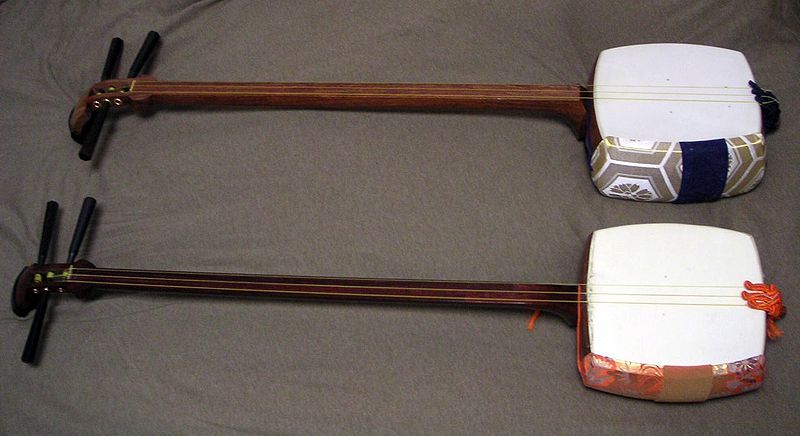

The Shamisen is a Japanese three-stringed instrument with a long neck and a drum-like body covered with skin. It is played with a plectrum called a bachi, creating a bright, percussive sound. The Shamisen is used in various traditional Japanese music genres, including folk, classical, and theater music such as kabuki and bunraku. It has a distinctive, expressive sound that reflects the cultural heritage and aesthetic principles of Japanese music, making it a symbol of traditional Japanese performing arts.
13. Hulusi
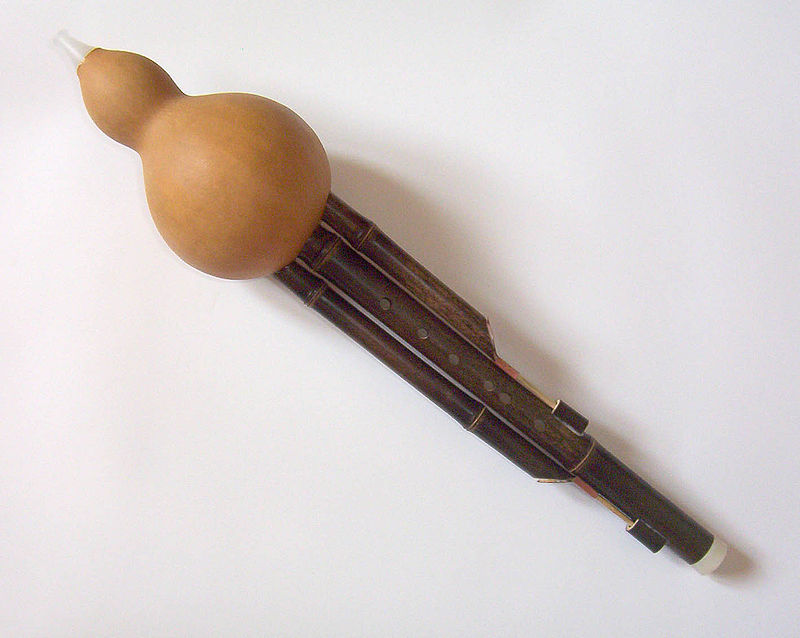

The Hulusi is a Chinese wind instrument made from bamboo and shaped like a gourd. It is popular in the folk music of China’s ethnic minority groups, especially among the Dai people. The Hulusi has a mellow, haunting tone that resembles a clarinet or ocarina, and it’s often used for playing lyrical and expressive melodies. It usually has three pipes: a main pipe with finger holes for melodies, and two drone pipes that either provide harmony or remain silent. The body of the Hulusi is often ornately decorated, and its soft, soothing sound makes it a favorite in solo performances and modern adaptations of traditional music.
14. Claviola
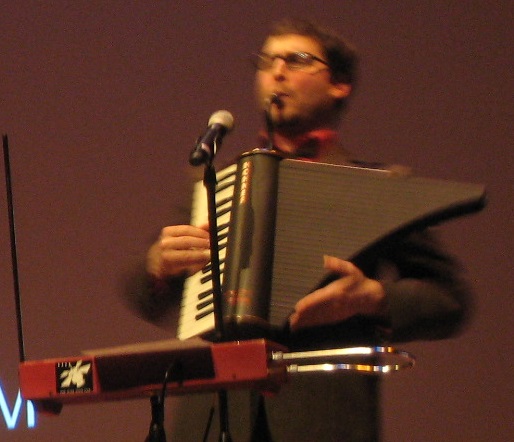

The Claviola, also known as the Key-Bagpipe, is a free-reed instrument developed in the mid-20th century. It combines elements of the accordion, harmonica, and melodica into a compact keyboard instrument. The Claviola is played by pressing keys that open and close valves, allowing air to pass through reeds inside the instrument, producing sound. It has a bright, cheerful tone and is used in various musical genres, from folk and traditional music to contemporary pop and rock. The Claviola’s portable design and expressive capabilities make it a versatile addition to both solo and ensemble performances.
15. Kemenche
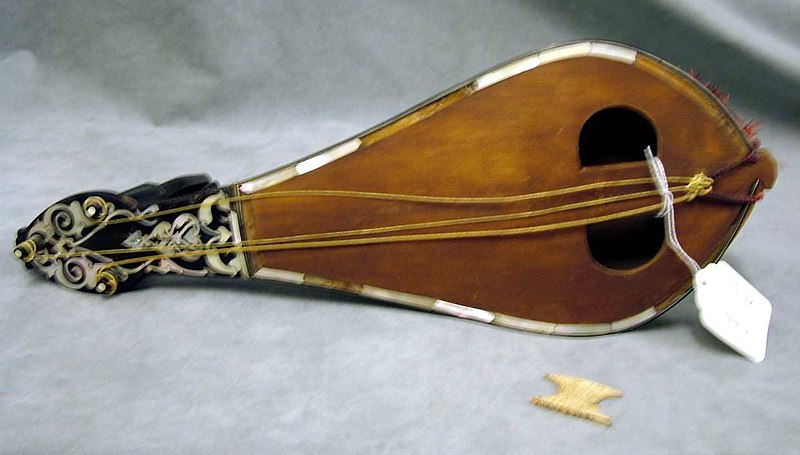

The Kemenche is a bowed string instrument from the Black Sea region of Turkey, as well as parts of Greece and the Middle East. It is closely associated with folk and classical music traditions in these areas. The instrument has a small, narrow body often made of wood, with three or four strings that are played using a bow. Known for its expressive and often melancholic sound, the Kemenche is played by holding it vertically, with the musician using one hand to press the strings and the other to control the bow. The Kemenche’s sound is haunting and deeply emotional, frequently used in dance music and evocative melodies.
16. Daegeum
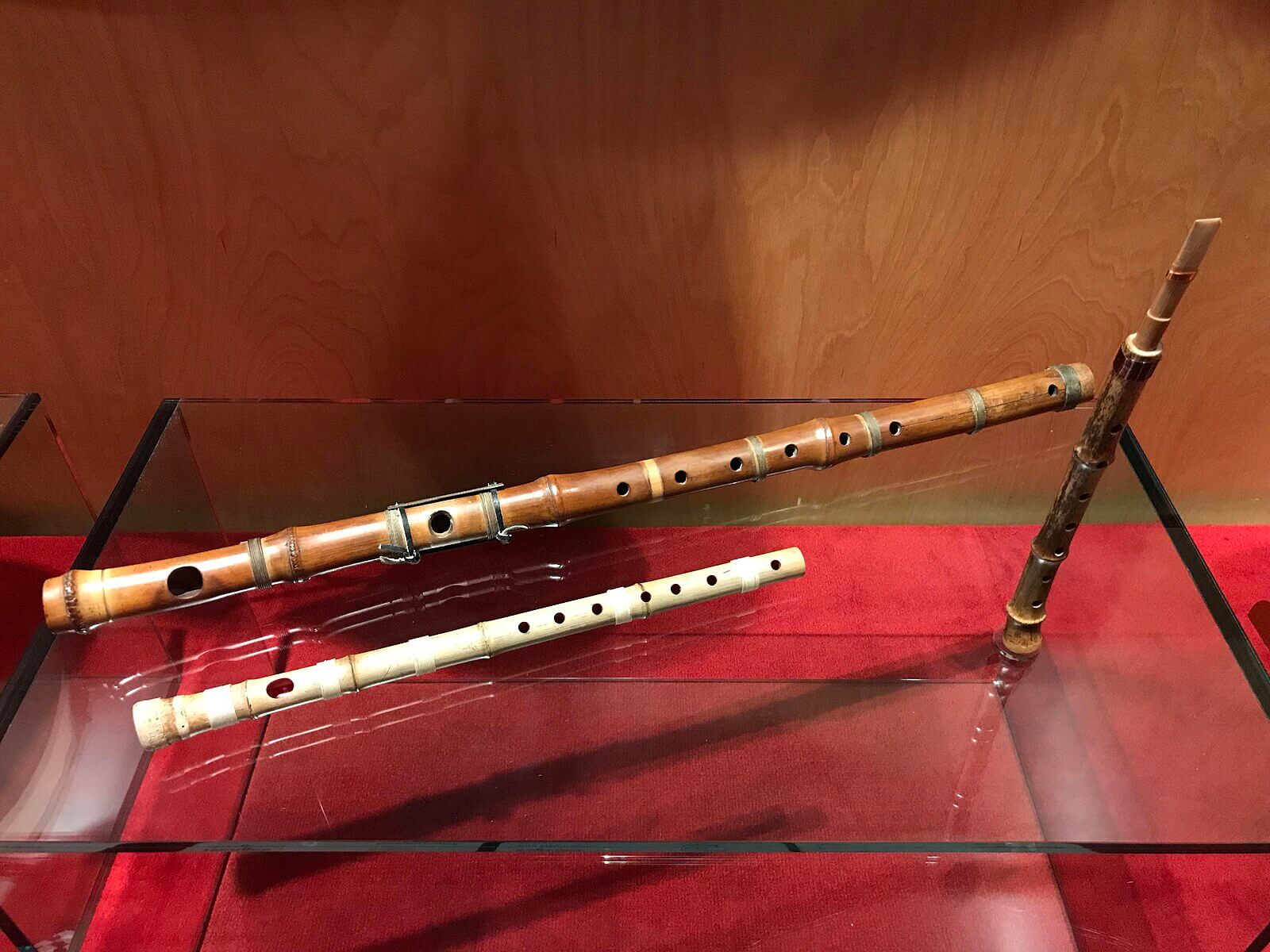

The Daegeum is a large Korean bamboo flute with a rich, resonant sound. It is an essential instrument in Korean classical music, court music, and folk traditions. The Daegeum is distinctive for its broad size and its ability to produce both deep, powerful tones and delicate, airy notes. The instrument is a long bamboo tube with six or seven finger holes and a buzzing membrane hole called a “cheong,” which gives the flute its unique vibrating timbre. The Daegeum is versatile, used in solo performances, as well as in orchestral and ensemble settings. Its sound can be calming or dramatic, depending on the style of music.
17. Ektara
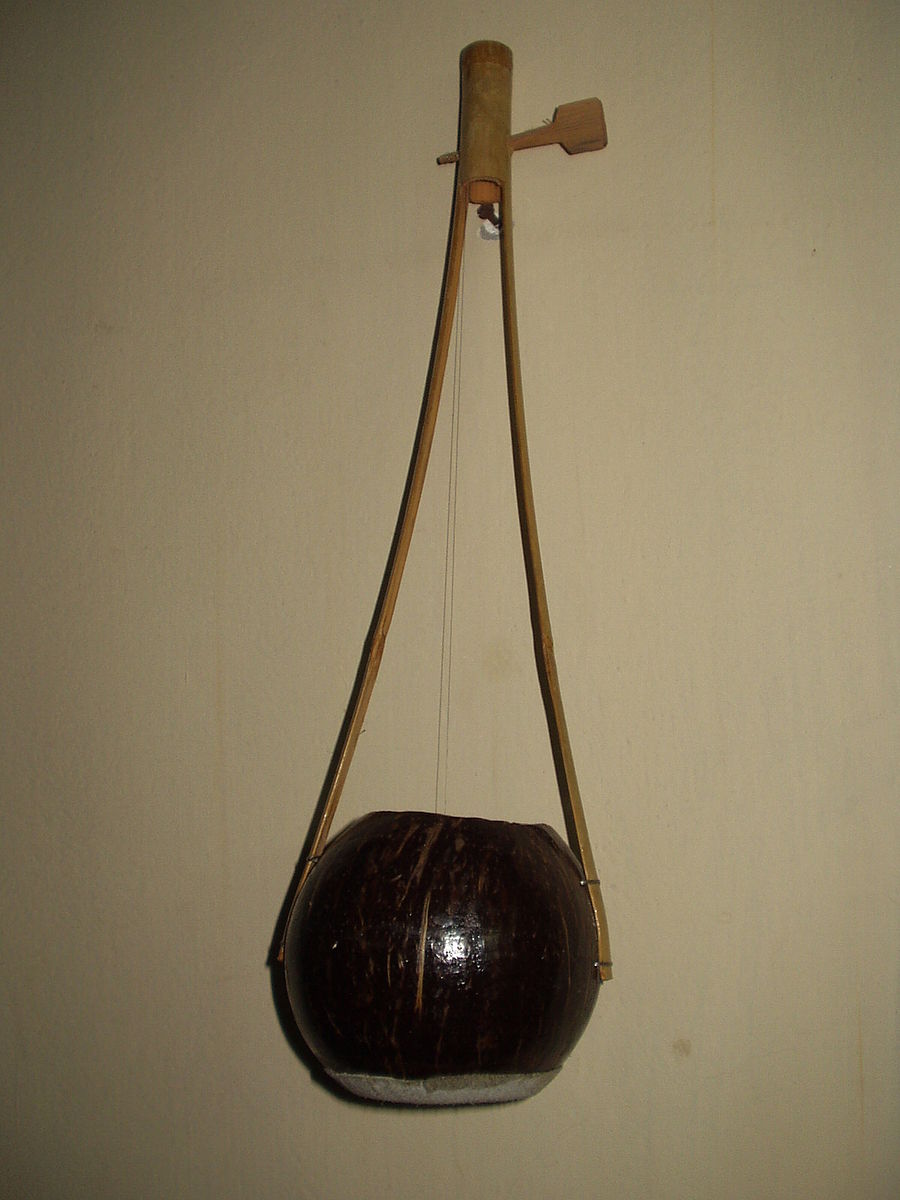

The Ektara is a one-stringed musical instrument traditionally used in folk music of South Asia, particularly in India, Bangladesh, and Pakistan. It has a long history and is often associated with wandering minstrels and devotional singers, particularly in the Baul and Sufi traditions. The instrument consists of a resonating chamber, usually made from a hollowed-out gourd or coconut shell, with a single string stretched across a bamboo or wooden neck. The player plucks the string while adjusting its tension by squeezing or releasing the neck, producing a distinctive, rhythmic drone sound. The Ektara’s simplicity and portability make it a popular instrument for solo performances, and it’s known for its meditative and soulful tone.
18. Hang
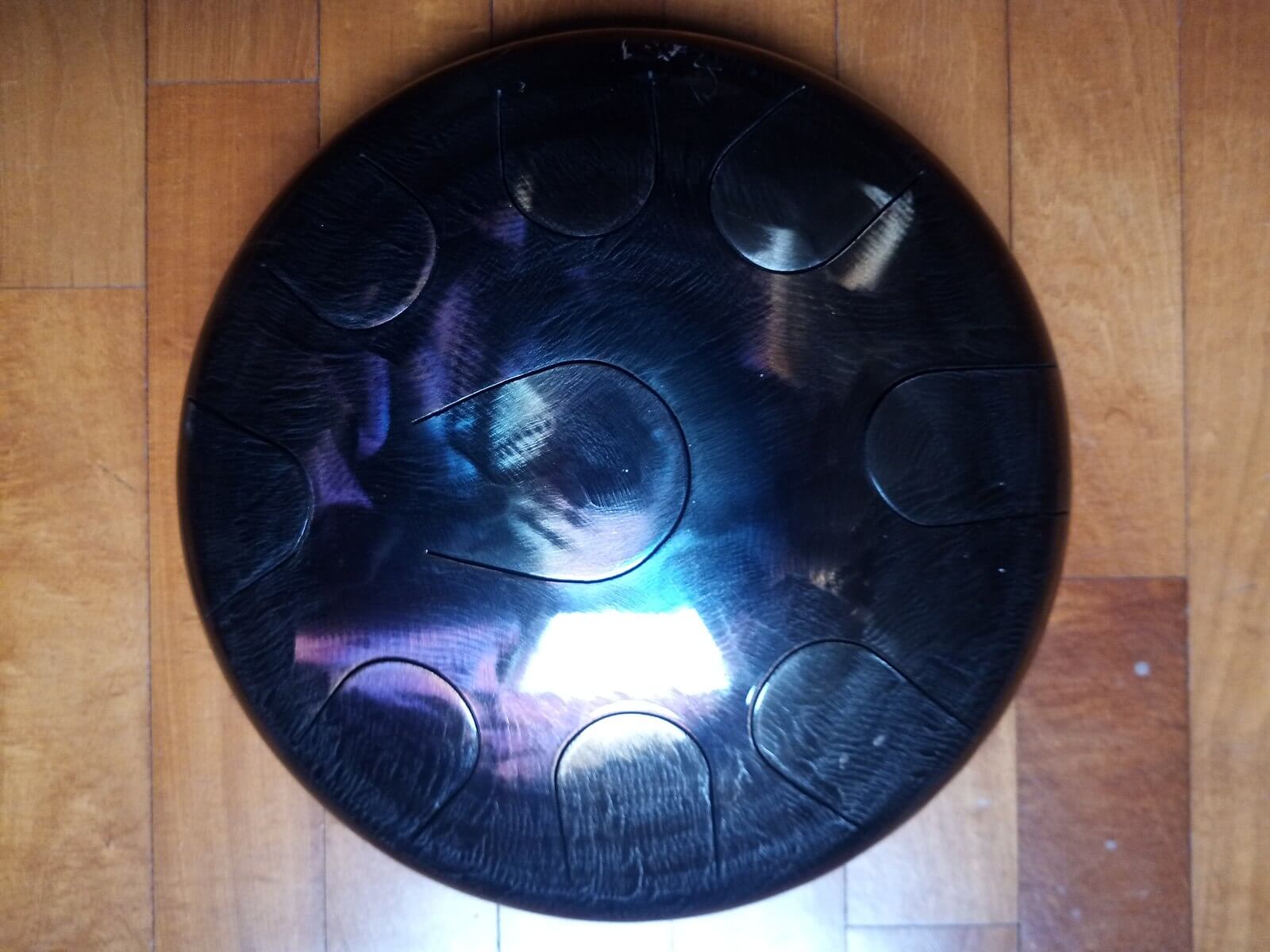

The Hang is a handcrafted percussion instrument created in Switzerland in the early 21st century. It consists of two hemispherical shells of nitrided steel glued together at the rim, creating a convex shape. The top shell has a center ‘note’ hammered into it and seven or eight ‘tone fields’ hammered around the center. These tone fields are tuned harmonically and are played with the hands. The Hang produces warm, resonant sounds that resemble bells or harmonically tuned steel drums. It has gained popularity worldwide for its soothing and meditative qualities.
19. Zurna
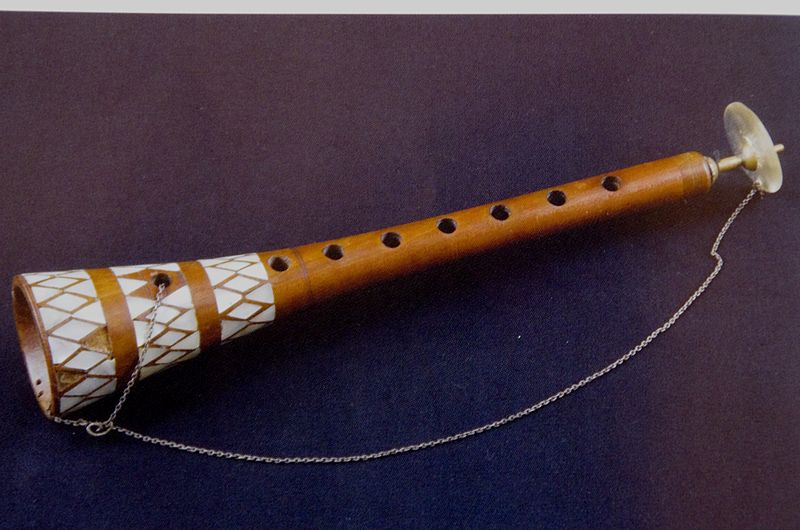

The Zurna is a wind instrument commonly used in the Middle East, Central Asia, and parts of the Balkans. It is a double-reed instrument, similar to an oboe, with a conical wooden body that typically features six finger holes. Known for its loud and penetrating sound, the Zurna is often used in folk music and ceremonial settings, such as weddings and festivals. The instrument produces a distinctive, reedy tone that can be both lively and expressive, making it well-suited for both melodic and rhythmic music. It is played by blowing air through the reeds while covering and uncovering the finger holes to create different pitches and tones.
20. Chapman Stick

The Chapman Stick is an electric string instrument invented by American jazz musician Emmett Chapman in the early 1970s. It features a long fretboard with 8 to 12 strings and is played by tapping or “hammering on” the strings with both hands. The Chapman Stick allows for polyphonic playing, enabling the musician to play bass, melody, and chords simultaneously. It is used in various genres, including jazz, rock, and experimental music, known for its versatility and expressive capabilities.
21. Sarangi
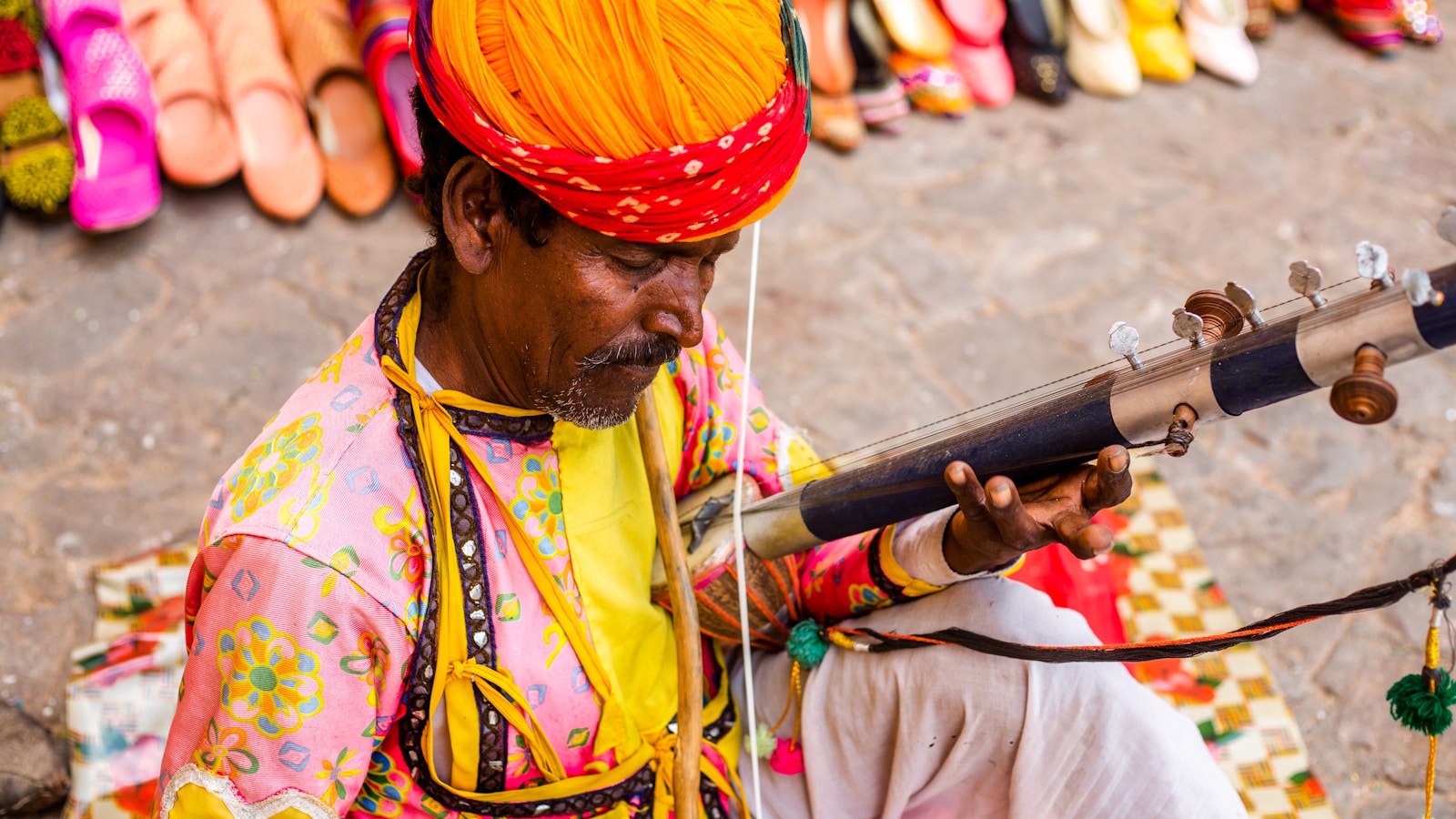

The Sarangi is a ancient bowed string instrument from the Indian subcontinent. It features a hollow wooden body with three main playing strings and up to 40 sympathetic strings. The Sarangi is played with a bow, and the strings are stopped not with the fingertips but with the nails or cuticles of the player’s left-hand fingers. It has a deeply emotional and vocal-like quality, often used in classical Indian music, folk music, and religious music. The Sarangi’s expressive capabilities allow for subtle nuances in pitch and tone, making it a revered instrument in Indian musical traditions.
22. Waterphone
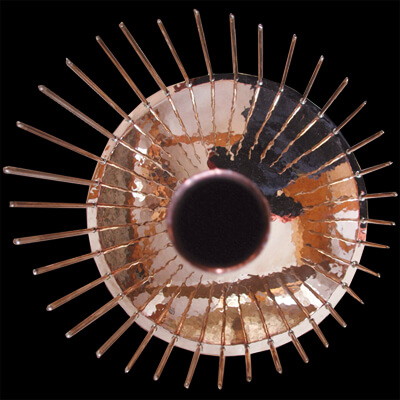
The Waterphone is a unique musical instrument invented by American painter and sculptor Richard Waters in the late 1960s. It consists of a stainless steel resonator bowl with a cylindrical neck and bronze rods of varying lengths and diameters attached around the rim. The Waterphone is played by bowing, striking, or rotating it, causing the rods to resonate and create eerie, ethereal sounds reminiscent of whale calls or otherworldly landscapes. It is used extensively in film scores, ambient music, and sound design for its haunting and evocative timbre.
23. Array Mbira

The Array Mbira is a modernized version of the traditional African mbira, featuring an expanded range of keys and a more complex structure. Unlike the smaller, more portable mbiras, which often have 22 to 28 metal tines (keys), the Array Mbira can have up to 150 tines, arranged in multiple rows to allow for greater musical possibilities. The instrument is played by plucking the tines with the thumbs, producing a bright, resonant, and often ethereal sound. The Array Mbira is known for its versatility, capable of producing intricate melodies and harmonies, and is used in both traditional African music as well as contemporary and experimental genres. Its rich, layered sound makes it suitable for solo performances or as an accompaniment in larger musical arrangements.
24. Shakuhachi
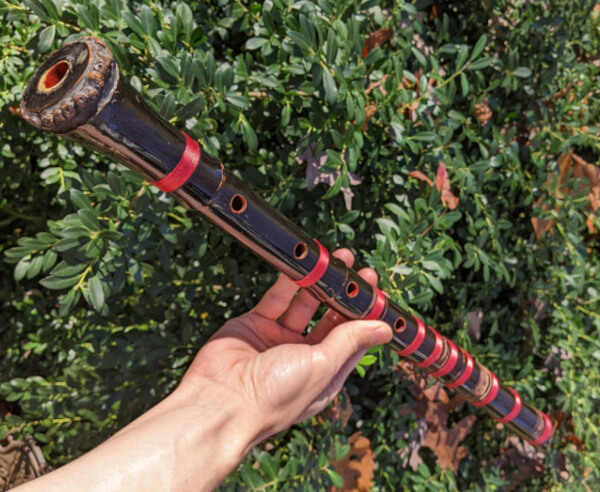

The Shakuhachi is a traditional Japanese bamboo flute with five finger holes and a distinctive notch cut into the blowing end. It has a rich history in Japanese Zen Buddhist meditation practices, as well as classical and folk music. The Shakuhachi is played by blowing air into the flute and using subtle variations in breath and finger placement to produce a wide range of tones and expressive nuances. It is known for its meditative and introspective sound qualities, making it a beloved instrument in Japanese cultural traditions.
25. Alphorn
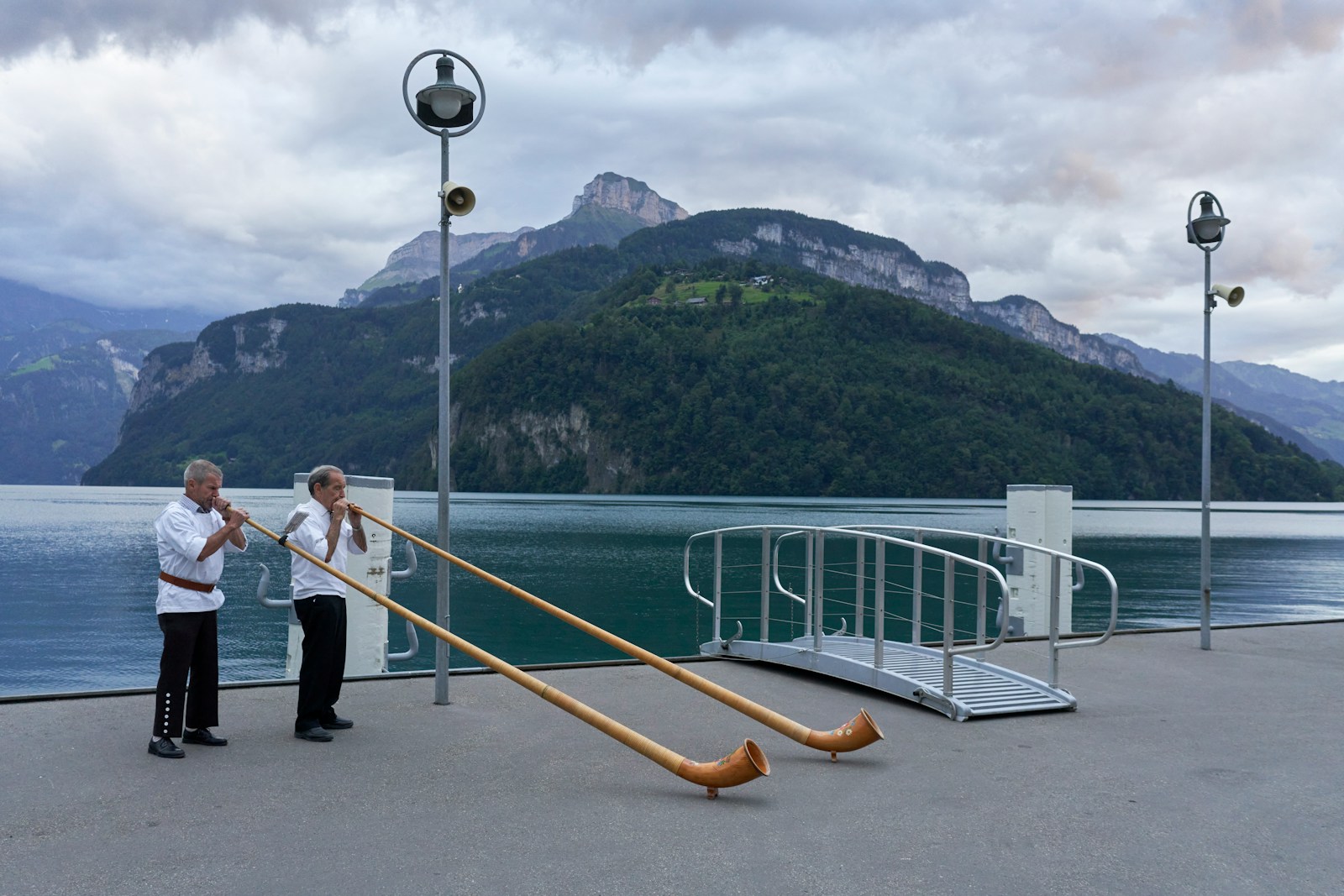

The Alphorn is a traditional wooden horn instrument used in mountainous regions of Europe, particularly in Switzerland, Austria, and Bavaria. It is typically made from a single piece of wood and can reach lengths of up to 13 feet (4 meters). The Alphorn produces deep, resonant tones and is played by blowing into a mouthpiece while the player’s hand adjusts the pitch by covering and uncovering the bell. It is used in folk music, alpine festivals, and ceremonial performances, symbolizing the natural beauty and cultural heritage of alpine regions.
26. Serpent
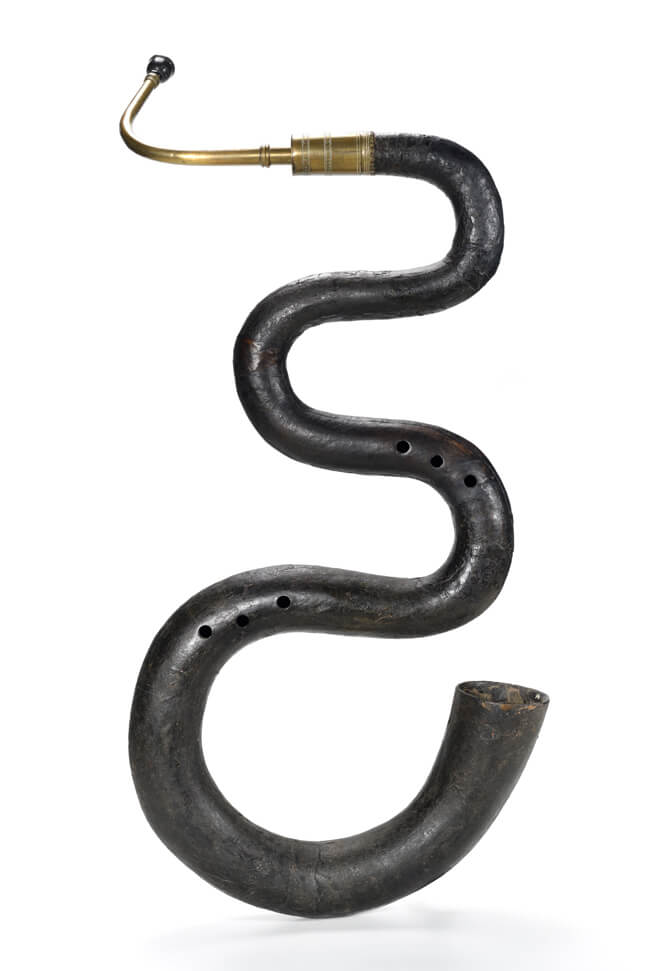

The Serpent is a historical brass instrument dating back to the 16th century. It features a coiled, snake-like shape, giving it its distinctive name. The Serpent has finger holes like a woodwind instrument but is played with a cup-shaped mouthpiece similar to that of a brass instrument. It produces a mellow, rounded sound and was historically used in church music and military bands. The Serpent has experienced revivals in early music ensembles and is appreciated for its unique timbre and historical significance.
27. Bandoneón
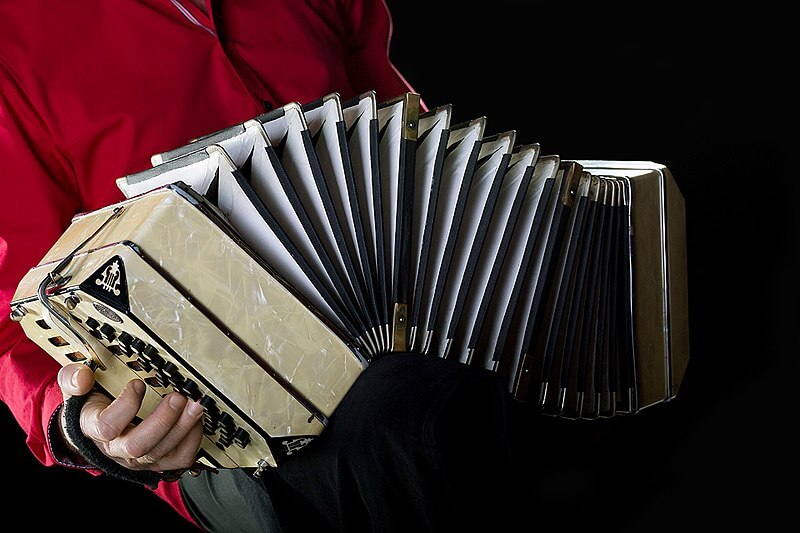

The Bandoneón is a type of concertina developed in Germany in the 19th century and later adopted in Argentina and Uruguay, where it became a central instrument in tango music. It features two rectangular wooden boxes connected by bellows and a series of buttons on both sides. The Bandoneón is played by expanding and contracting the bellows while pressing the buttons to produce different notes. It has a rich, expressive sound ideal for the passionate rhythms and melancholic melodies of tango music, making it an integral part of the genre’s distinctive sound.
28. Baryton

The Baryton is a rare string instrument from the 17th and 18th centuries, similar to the viola da gamba. It has six or seven gut strings played with a bow and an additional set of sympathetic metal strings that can be plucked with the thumb of the left hand. This dual functionality allows the Baryton to produce a rich, complex sound with both bowed and plucked tones. The instrument was popular in the Baroque and Classical periods, especially in the court of Prince Nikolaus Esterházy, who commissioned numerous compositions for it from the famous composer Joseph Haydn. Today, the Baryton is mainly of interest to early music specialists and enthusiasts who seek to revive its unique sound in historical performances.
29. Pipe Organ
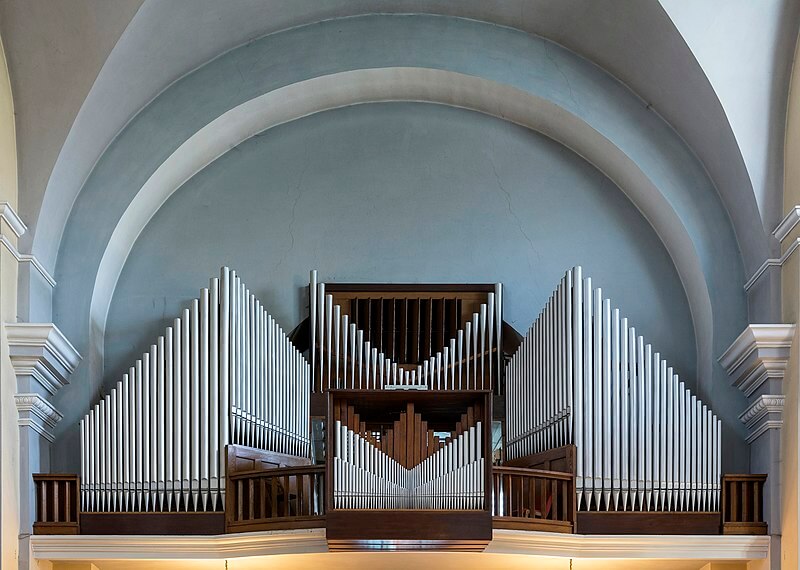

The Pipe Organ is a keyboard instrument that produces sound by driving pressurized air through pipes of various lengths and materials. It is known for its majestic and powerful sound, capable of filling vast spaces with music. The Pipe Organ has a long history dating back to ancient Greece and Rome, evolving over centuries into the complex instruments found in churches, cathedrals, and concert halls today. It is used in religious ceremonies, classical music performances, and organ recitals, prized for its ability to evoke a range of emotions and its impressive sonic capabilities.
30. Yaybahar
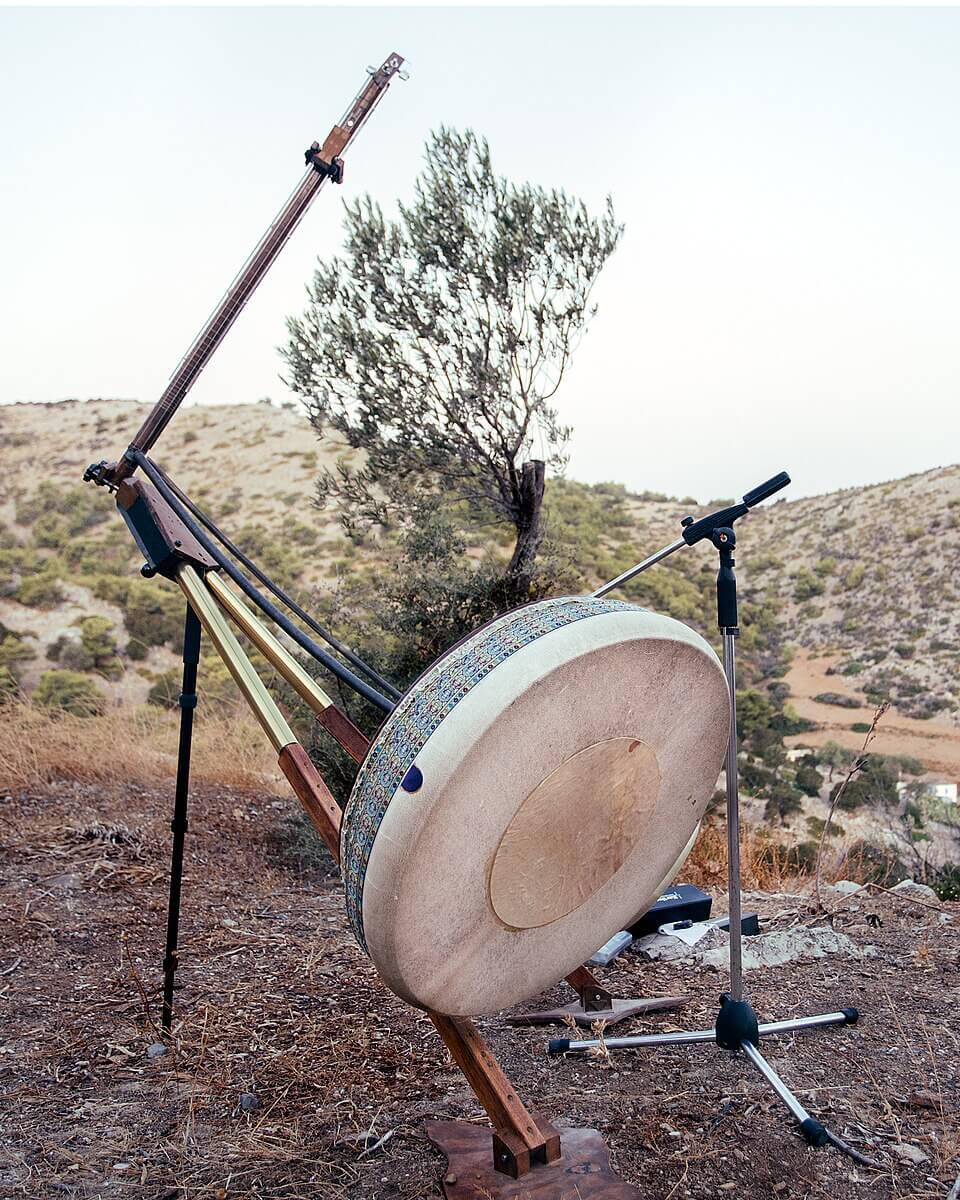

The Yaybahar is an acoustic instrument designed by Turkish musician Görkem Şen. It consists of a wooden frame with strings stretched across it, connected to two drum-like membranes. The vibrations from the strings are transmitted through these membranes, which are then amplified acoustically. The Yaybahar produces a diverse range of sounds, from deep bass tones to sharp percussive notes, resembling a blend of string and percussion instruments. It is played by plucking or bowing the strings and has gained attention for its unique design and sonic capabilities.
Think you know world culture? Explore our quiz hub and test yourself on fascinating facts from around the globe.
Daniel Zohar is a passionate entrepreneur and digital marketing expert with a strong focus on business and affiliate marketing. With over 10 years of experience in the industry, he has gained valuable insights and strategies that he is eager to share with others. Through his writing and speaking, Daniel aims to help others achieve success in business and affiliate marketing, using his own experiences as a guide. In addition to his work as a writer and speaker, he is a successful business owner and consultant, helping companies and individuals reach their goals in the digital world.
You Might Also Like:
- How to Find the Right Influencer for Your Brand
June 23, 2024 - 9 Best Niches for Affiliate Marketing in 2025
January 7, 2025 - 16 Affordable Hosting Options for Your Blog in 2025
February 21, 2025 - Comedy Sells: How to Make Your Business Memorable with Humor
January 6, 2023 - 100 of the Most Beautiful Words in the English Language
April 8, 2024
